How Can Investors Capture The Humanoid Robotics Investment Opportunity?
By Cole Wenner
Humanoid robots are beginning to enter the global economy. At this very moment, humanoids are delivering packages, assisting in factory assembly lines, and working in warehouses. However, we believe the next wave of robotics promises even greater integration, with robots poised to become familiar presences in our daily lives.
The KraneShares Global Humanoid and Embodied Intelligence Index ETF (Ticker: KOID) aims to capture investment opportunities resulting from the rise of global humanoid robotics and embodied intelligence. Unlike many legacy robotics‐focused ETFs, KOID represents the first US-listed thematic equity ETF that focuses on the global humanoid opportunity.1
The Case for the Human Form & Key Application Scenarios
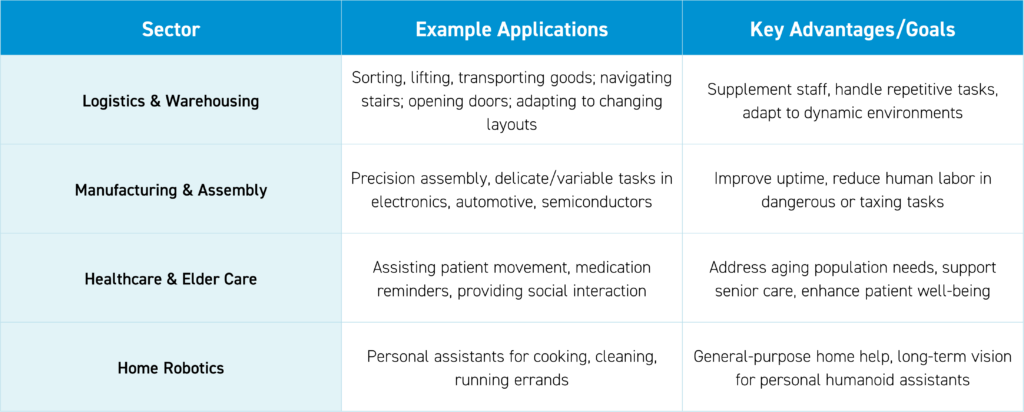
Humanoid robots are rapidly moving from science fiction to practical reality, transforming sectors from manufacturing and logistics to healthcare and home assistance. Humanoid robots, designed to mimic the form and function of the human body, offer a key advantage: they can operate in environments already built for people. That means there is no need to redesign factories, warehouses, or retail spaces; they should be able to be plugged into these settings with minor adjustments.
Companies like Amazon, Tesla, and BYD are piloting humanoids in warehouses and envisioning them as future home assistants, while healthcare providers look to these robots to support aging populations and deliver essential care. As adoption accelerates, we believe humanoid robots are poised to reshape the workforce, improve safety and efficiency, and address critical labor shortages across multiple industries.
Embodied Intelligence: AI That Moves
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) have made the marriage of robotics with embodied intelligence possible, systems that can learn as they interact with the physical world. Unlike traditional AI trained solely on text or static data, embodied AI continuously learns from its surroundings, enabling robots to adapt to complex tasks and dynamic environments. This means intelligent machines should be able to follow commands, but also make decisions, improve over time, and even collaborate with human coworkers.

Labor Shortages & Economic Pressure
Behind the sudden surge in humanoid robotics is a cocktail of macroeconomic tailwinds: aging workforces in many countries, persistent labor shortages in physically demanding jobs, and rising wages in key markets. For businesses under pressure to reduce costs and increase productivity, humanoid robots present a long-term hedge against human capital volatility. Humanoid robots could likely fill the gaps no one else wants to.
Market Projections: A $5 Trillion Opportunity
Morgan Stanley believes Humanoids could have nearly a $5 Trillion Total Addressable Market by 2050 globally.2 That forecast assumes steady improvements in cost efficiency, mobility, and general-purpose AI.
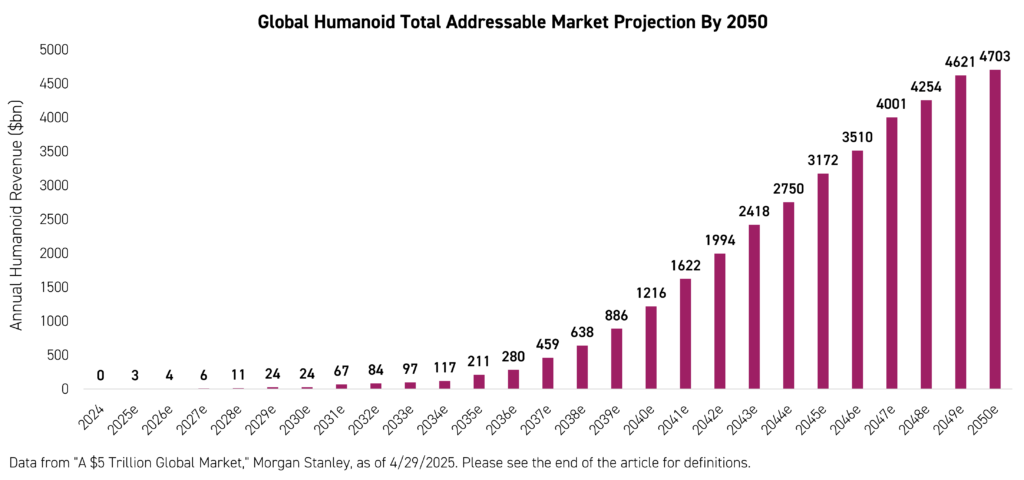
Morgan Stanley is not the only major institution that is projecting sizable growth for Humanoids. Goldman Sachs estimates that the global humanoid robot market could surpass $150 billion in revenue annually by 2035, with commercial adoption accelerating sharply after 2025.3 In the near term, use cases could be highly targeted, but the longer-term vision is sweeping: a potentially versatile robotic labor force that may be capable of performing tasks in environments designed for people.
Where is the value in today’s robotics market?
As investment in humanoid robotics intensifies, the early phases of this technological surge are anticipated to see "enablers", the providers of core technologies and manufacturing capabilities, capture a significant portion of the value. The drive to commercialize humanoid robots is highlighting the importance of the industrial backbone that supports this advancement. Successfully building general-purpose humanoid robots is not solely an AI challenge; it demands a complex, interdisciplinary manufacturing ecosystem encompassing areas from actuation and motion control to sensing and strategic materials like rare earths.
Investment opportunities lie within this foundational ecosystem:
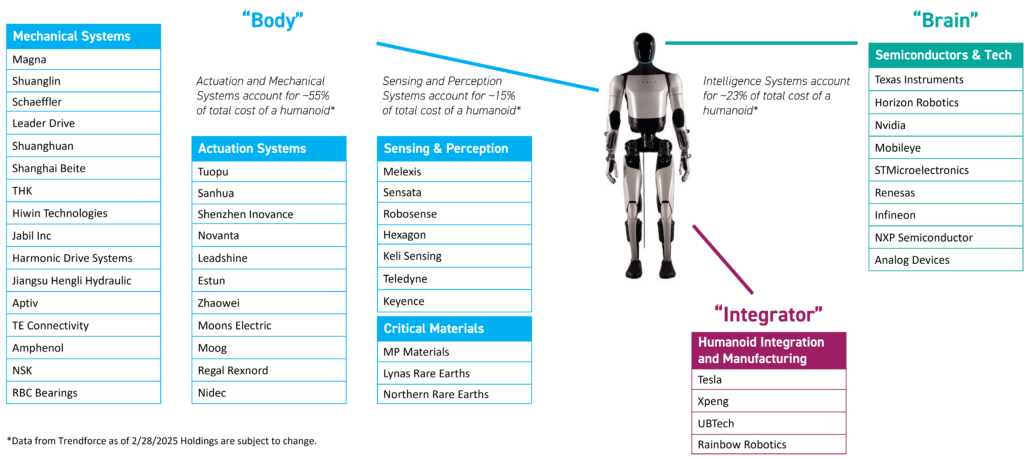
The "Brain": Powering Intelligent Autonomy
The cognitive capabilities of humanoid robots, enabling them to perceive, decide, and interact, reside in their "brain."
Embodied Intelligence Technology & AI Chips: High-performance, low-power computing is paramount for real-time AI inference, sophisticated vision processing, and precise robotics control. Specialized silicon, including advanced AI chips, vision processors, compute units, memory, and analog components, forms the core of this brainpower. We believe investment in these custom semiconductor solutions is crucial for enabling the onboard intelligence humanoids require.
For example, Nvidia (2.52% weight in KOID as of 6/20/2025) is powering the brains of humanoid robots with its Isaac GR00T platform, a suite of open, customizable AI foundation models designed specifically for generalized humanoid reasoning and skills. The GR00T N1 model features a dual-system architecture inspired by human cognition, combining fast, reflexive decision-making with slower, deliberate reasoning, enabling robots to adapt, learn, and perform complex tasks in dynamic environments. This AI "brain" is trained on vast datasets, including real and synthetic motion data. Developers use Nvidia’s simulation tools, like Isaac Sim and Isaac Lab, to train and validate robot behaviors in virtual environments before real-world deployment, accelerating the path toward truly capable, general-purpose humanoids.
The "Body": Enabling Physical Interaction and Mobility
The physical form and capabilities of humanoid robots depend on an array of components that constitute their "body."
Actuation and Mechanical Systems: Actuators are the devices that convert energy into mechanical motion, serving as the essential "muscles" of humanoids. Every joint, from its fingertips to knees, relies on actuators, such as motors, gears like harmonic drives, and bearings, to deliver precise control, combining strength, speed, and energy efficiency. The demand for high degrees of freedom, dynamic balance, and human-like dexterity in humanoids places stringent requirements on next-generation actuators, which must be compact, lightweight, and scalable for mass production.
Regal Rexnord (2.31% weight in KOID as of 6/20/2025), a U.S. based manufacturer specializing in automation and motion control parts, supplies components like high-performance motors, bearings, and gear reducers that enable precise, human-like movement in robots; its expertise in precision motion control and scalable manufacturing has already made it a key global supplier to leading humanoid robot makers.
Sensing & Vision Systems: Humanoids depend on an array of high-fidelity sensing systems to achieve real-time situational awareness. These include visual cameras, depth sensors (such as LiDAR and stereo vision systems), tactile sensors for interaction feedback, microphones for auditory input, and inertial measurement units (IMUs) for balance and orientation. These components are the primary interfaces through which the robot perceives and interacts with its environment.
Melexis NV (2.62% weight in KOID as of 6/20/2025), headquartered in Belgium with locations in countries like France, Germany, Switzerland, and the U.S., develops advanced sensor technologies—such as its Tactaxis® tactile sensor and high-resolution magnetic encoders—that give robots a sense of touch and precise positional awareness, enabling them to safely and delicately interact with their environment much like humans do. Its compact, robust, and cost-effective sensors, which can detect fine force changes and are immune to magnetic interference, are essential for tasks requiring dexterity and sensitivity, making Melexis a notable enabler for the next generation of intelligent, human-like robots.
Critical Materials: Humanoid robots, particularly their high-torque permanent magnet motors essential for actuators and mobility, are heavily reliant on rare earth elements like neodymium and dysprosium. The concentrated nature of the global supply chain for these materials presents a strategic risk and an area of focus for ensuring sustainable production.
MP Materials (2.93% weight in KOID as of 6/20/2025), newly founded in 2017, is critical for the U.S. humanoid industry because it is the only domestic producer of rare earth metals and magnets—especially neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets—which are essential for the powerful, precise actuators in humanoid robots.
MP Materials CEO Jim Litinsky stated during the company's Q1 2024 earnings call that "Humanoid robots will have double or triple the magnetic content of an EV" as each robot requires "dozens of actuators" powered by rare earth magnets.4
By restoring a fully integrated US supply chain for these vital components, MP Materials reduces reliance on foreign sources, strengthens national security, and supports the scalable growth of the American robotics sector.
The "Integrators": Assembling the Future
Integrators are the companies at the forefront of designing, developing, and manufacturing complete humanoid robots. They bring together the complex array of "Brain" and "Body" components, often drawing on expertise from diverse industries like automotive, consumer electronics, and existing robotics. These entities play a pivotal role in translating foundational technologies into commercially viable humanoid solutions.
Tesla (2.39% weight in KOID as of 6/20/2025) is advancing its Optimus robot with proprietary AI and hardware for autonomous, general-purpose tasks in factories and beyond. XPeng (1.73% weight in KOID as of 6/20/2025) is investing heavily in its Iron humanoid, aiming for mass production and industrial deployment to transform automation in manufacturing, retail, and healthcare. UBTech (1.82% weight in KOID as of 6/20/2025), who serves customers worldwide from its Shenzhen headquarters, is leveraging partnerships and AI, has become a leading deployer of humanoids in automotive factories, and is expanding into service and consumer sectors with emotionally intelligent robots. South Korea's Rainbow Robotics (2.31% weight in KOID as of 6/20/2025), who operates robot manufacturing businesses, offers a modular, research-oriented humanoid platform (RB-Y1) with advanced mobility and open software development kits (SDKs), targeting both academic and industrial applications while benefiting from Samsung’s strategic backing.
Challenges of Building a Global Thematic ETF in Humanoid Robotics
Constructing a global thematic ETF focused on humanoid robotics and embodied intelligence presents unique challenges. The sector is rapidly evolving, with technological leadership distributed across multiple regions and industries. Traditional robotics ETFs often concentrate in a few large-cap names or geographic regions, potentially missing the full breadth of innovation and value creation occurring throughout the ecosystem.
A critical challenge is ensuring that the portfolio captures not just the most visible robot manufacturers, but also the enablers—the companies supplying the core technologies and materials that make advanced robotics possible. Many of these enablers are specialists or mid-cap companies outside the typical large-cap universe. Additionally, the global nature of the humanoid robotics supply chain means that holdings have to be sourced from around the world and evaluated for both their domestic and global impact. Thematic ETFs must prioritize inclusion of the industry’s top-ranking companies, regardless of their country of origin, to ensure comprehensive and representative exposure to the sector.
KOID’s Approach: Equal-Weighted, Broad-Based Exposure
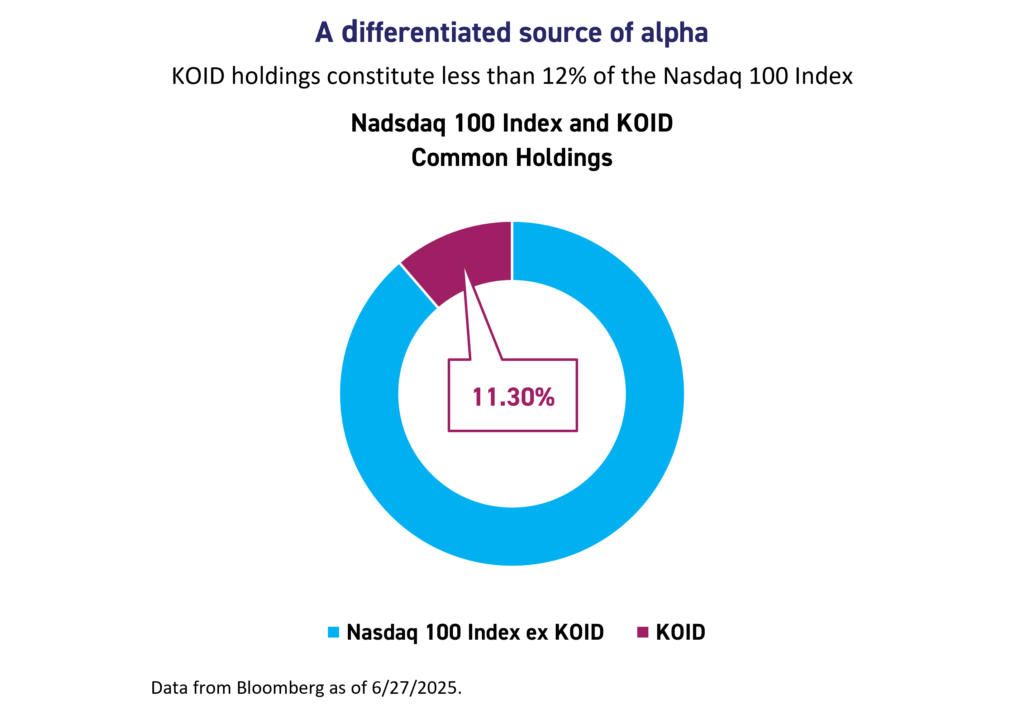
KOID addresses these challenges by employing an equal-weighted portfolio strategy that rebalances quarterly and currently encompasses 51 companies across six key categories. This approach ensures that no single company or country dominates the fund, providing investors with a balanced representation of the entire humanoid robotics ecosystem. Additionally, KOID offers investors unique exposure compared to major technology-focused indexes like the Nasdaq 100, with only an 11.3% holdings overlap according to data from Bloomberg.5 This means that investors gain access to a distinct set of companies—many of which are not included in mainstream technology indexes—and, even where there is overlap, the equal-weight methodology prevents overconcentration in any single company.
By utilizing a proprietary “Humanoid and Embodied Intelligence Exposure Score,” KOID selects companies based on their actual participation in the development or supply chain of humanoid robotics, not just their headline status or market capitalization. This methodology is designed to deliver targeted exposure to the global humanoid opportunity, capturing the full spectrum of technological advancement and enabling investors to participate in the growth of this emerging sector from all angles.
Conclusion
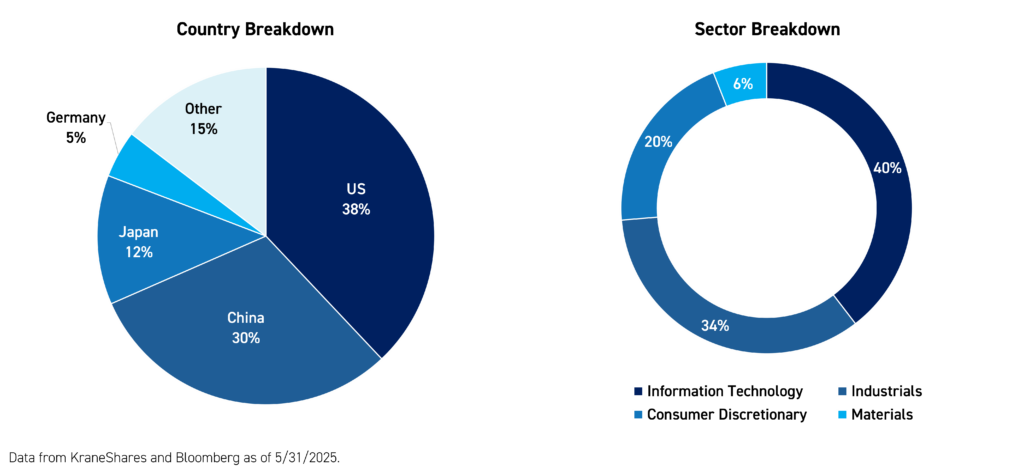
KOID invests across the full spectrum of the humanoid ecosystem, including the “brain” of the humanoid (semiconductors & technology), the “body” of the humanoid (actuation systems, mechanical systems, sensing & perception, critical materials), and humanoid “integrators” & manufacturing companies. KOID offers global exposure to companies based primarily in the United States, China, and Japan that are included in the information technology, industrial, and consumer discretionary sectors.
Holdings are subject to change.
For KOID standard performance, top 10 holdings, risks, and other fund information, please click here.
Citations:
- Data from Bloomberg as of 5/27/2025.
- “Humanoids: 1bn Robots and $5tn Revenues by 2050, China is in Pole Position,” Morgan Stanley Research, 4/28/2025.
- "Global Automation: Humanoid Robots," Goldman Sachs, 2/2/2025.
- Data from MP Materials company website and 2024 Q1 earnings call transcript.
- Data from Bloomberg as of 6/27/2025.
* All holding weight % data is from Bloomberg as of 6/20/2025.
Definitions:
Revenue: The total amount of money a company earns from its sales of goods or services before any expenses are deducted.
Total Addressable Market (TAM): The overall revenue opportunity available for a product or service if it achieved 100% market share within a specific market.
Alpha: A measure of an investment's performance relative to a benchmark index, representing the excess return generated by that investment.
Index Definitions:
Nasdaq 100 Index: The Nasdaq-100 is a stock market index made up of equity securities issued by 100 of the largest non-financial companies listed on the Nasdaq stock exchange. It is a modified capitalization-weighted index. The Nasdaq 100 Index is commonly used as a comparison for technology funds because it is heavily weighted toward technology and innovative growth companies, making it a widely recognized benchmark for tracking the performance and trends of the tech sector.